Crop gap definition ap human geography – As the concept of crop gap definition takes center stage in AP Human Geography, this analysis embarks on an in-depth exploration of its multifaceted nature. By unraveling the factors that contribute to crop gaps and examining their consequences, this discourse provides a comprehensive understanding of this critical issue.
Crop gaps, the disparity between potential and actual crop yields, pose significant challenges to global food security. Understanding their causes and consequences is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
Crop Gap Definition
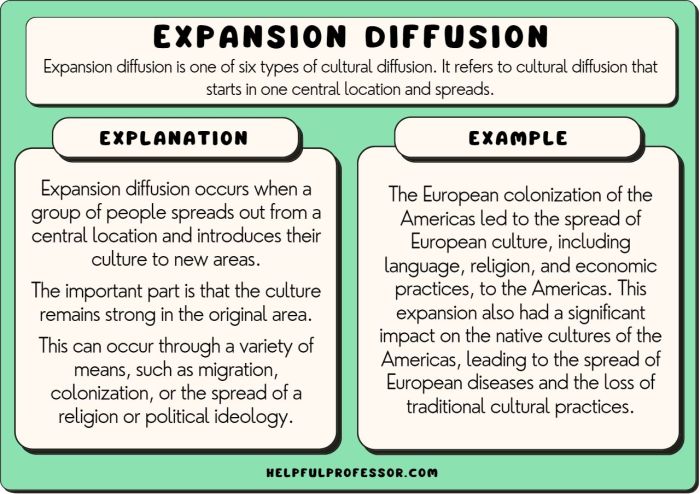
A crop gap is the difference between the potential yield of a crop and the actual yield achieved in a given area. This gap can arise due to a variety of factors, including climate, soil conditions, agricultural practices, economic constraints, and political policies.
Causes of Crop Gaps: Crop Gap Definition Ap Human Geography
Crop gaps can be attributed to a combination of natural and human-induced factors. Natural factors include unfavorable climatic conditions, such as extreme temperatures, drought, or flooding, which can damage crops or reduce their productivity. Soil conditions, such as nutrient deficiencies or poor drainage, can also limit crop yields.
Human-induced factors include inadequate agricultural practices, such as improper irrigation, fertilization, or pest management. Economic constraints, such as lack of access to capital or technology, can prevent farmers from investing in necessary inputs to improve yields. Political policies, such as trade barriers or government subsidies, can also affect crop production and contribute to crop gaps.
Consequences of Crop Gaps
Crop gaps have significant negative consequences for food security, the environment, and socio-economic development. Food insecurity occurs when people do not have access to sufficient food to meet their nutritional needs. Crop gaps can exacerbate food insecurity by reducing the availability of food and increasing prices.
Environmental implications of crop gaps include soil degradation, water scarcity, and loss of biodiversity. Unsustainable agricultural practices to close crop gaps can lead to soil erosion, water pollution, and deforestation. These environmental impacts can further reduce crop yields and exacerbate food insecurity.
Socio-economic costs of crop gaps include poverty, malnutrition, and social unrest. Farmers who cannot achieve their potential yields may face financial losses and reduced income, leading to poverty and food insecurity. Malnutrition can result from a lack of access to diverse and nutritious foods, which can have long-term health consequences.
Strategies to Reduce Crop Gaps

Reducing crop gaps requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both natural and human-induced factors. Improving agricultural technology, such as developing drought-resistant crop varieties or precision farming techniques, can help farmers overcome climatic challenges and increase yields.
Promoting sustainable farming practices, such as crop rotation, mulching, and conservation tillage, can improve soil health and reduce environmental impacts while maintaining or increasing yields. Investing in infrastructure, such as irrigation systems or transportation networks, can also help farmers access markets and improve their ability to produce crops.
Addressing economic constraints and providing access to capital and technology can enable farmers to invest in improved agricultural practices and increase their yields. Policy interventions, such as agricultural subsidies or crop insurance, can also provide incentives for farmers to adopt sustainable practices and reduce crop gaps.
FAQs
What is the primary cause of crop gaps?
Crop gaps primarily result from a combination of factors, including unfavorable climate conditions, poor soil quality, inadequate agricultural practices, and economic or political constraints.
How do crop gaps impact food security?
Crop gaps directly contribute to food insecurity by reducing the availability of staple crops, leading to higher food prices and malnutrition, particularly in vulnerable populations.
What are some effective strategies to reduce crop gaps?
Effective strategies to reduce crop gaps include improving agricultural technology, promoting sustainable farming practices, and addressing economic and political barriers that hinder agricultural productivity.