Introducing the anatomy of the constitution worksheet answers, a comprehensive guide that unveils the intricate workings of the United States Constitution. This indispensable resource provides a thorough examination of the Constitution’s structure, principles, and historical significance, empowering individuals to navigate its complexities with confidence.
Delving into the anatomy of the Constitution, we explore the powers and responsibilities of each branch of government, the fundamental freedoms guaranteed by the Bill of Rights, and the dynamic nature of a living Constitution that adapts to the evolving needs of society.
Through engaging discussions and insightful analysis, this guide illuminates the Constitution’s enduring legacy and its profound impact on American democracy.
1. Overview of the Anatomy of the Constitution
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It establishes the framework for the federal government, defines the fundamental rights of citizens, and Artikels the process for amending the document.
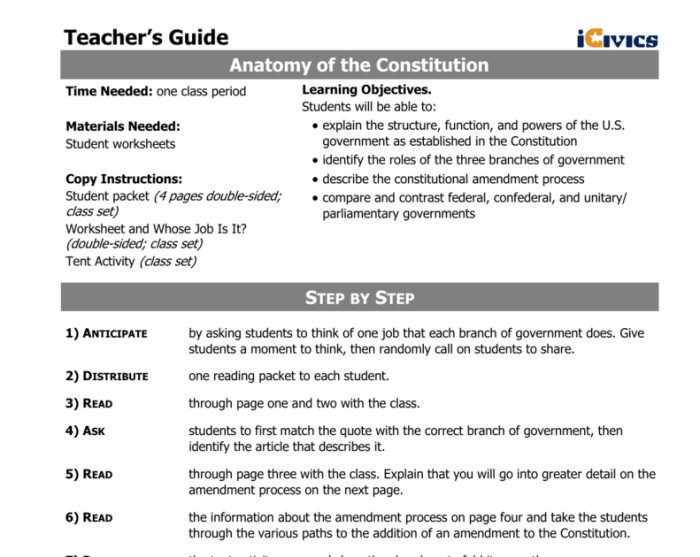
The Constitution is divided into seven articles, each addressing a specific aspect of government. The first three articles establish the three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
2. Article I
Legislative Branch
Article I establishes the legislative branch, consisting of the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives is composed of members elected from each state, based on population. The Senate is composed of two senators from each state.
The legislative branch has the power to make laws, declare war, and impeach the President. It also has the power to approve treaties and confirm presidential appointments.
3. Article II
Executive Branch
Article II establishes the executive branch, headed by the President. The President is elected by the Electoral College and serves a four-year term. The President is responsible for enforcing laws, appointing officials, and conducting foreign policy.
The executive branch also includes the Cabinet, which is composed of the heads of the various executive departments. The Cabinet advises the President and assists in the administration of the government.
4. Article III
Judicial Branch
Article III establishes the judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States and has the power to interpret the Constitution and laws.
The judicial branch also includes lower federal courts, which handle cases involving federal law. The federal courts have the power to declare laws unconstitutional.
FAQ Overview: Anatomy Of The Constitution Worksheet Answers
What is the purpose of the Constitution?
The Constitution establishes the framework for the United States government, defines the fundamental rights of citizens, and Artikels the principles of American democracy.
How many articles are there in the Constitution?
The Constitution consists of seven articles, each addressing different aspects of government structure and powers.
What is the significance of the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights (first ten amendments) guarantees essential freedoms and protections for individuals, including freedom of speech, religion, and the right to a fair trial.
