Comparing cell organelles a cell color by number answer key sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Delve into the fascinating world of cell organelles, where each vibrant hue unveils a distinct function, contributing to the intricate symphony of life.
Our journey begins with a comprehensive exploration of the diverse cast of cell organelles, each playing a pivotal role in the cell’s survival and well-being. We will uncover their unique colors, unravel their intricate functions, and witness the remarkable interactions that orchestrate cellular harmony.
Introduction to Cell Organelles: Comparing Cell Organelles A Cell Color By Number Answer Key
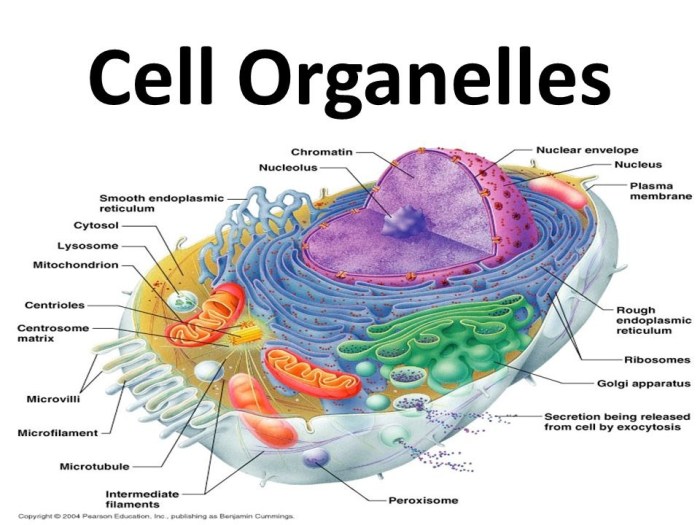
Cell organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions essential for the cell’s survival and functioning. Each organelle has a unique structure and composition that enables it to carry out its specific role.
There are various types of organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Each organelle has a specific function that contributes to the overall functioning of the cell.
Comparing Cell Organelles by Color, Comparing cell organelles a cell color by number answer key
| Organelle Name | Color | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Brown | Contains genetic material and controls cell activities | [Image of nucleus] |
| Mitochondria | Red | Produces energy for the cell | [Image of mitochondria] |
| Ribosomes | Green | Synthesizes proteins | [Image of ribosomes] |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Blue | Processes and transports proteins | [Image of endoplasmic reticulum] |
Cell Organelles and Their Functions

Nucleus:The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and directing cellular activities.
Mitochondria:Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes:Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, translating genetic information into proteins.
Endoplasmic Reticulum:The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein processing, folding, and transportation.
Organelle Interactions
Cell organelles do not function in isolation but interact with each other to maintain cellular homeostasis. For example, the endoplasmic reticulum modifies proteins synthesized by ribosomes, and the Golgi apparatus further processes and packages these proteins for transport.
Organelle Diseases
Malfunctioning organelles can lead to various diseases and disorders. For example, mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
User Queries
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a complex network of membranes that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage.
How do cell organelles interact with each other?
Cell organelles engage in intricate interactions, exchanging molecules and signals to maintain cellular homeostasis and orchestrate the cell’s overall functioning.