A treasury yield curve plots treasury interest rates relative to: – A treasury yield curve plots treasury interest rates relative to maturity, providing a graphical representation of the relationship between the two. This curve serves as a crucial tool for investors, economists, and policymakers, offering insights into economic trends and guiding investment decisions.
Treasury yield curves are constructed by plotting the yields of Treasury securities with varying maturities on a graph. The resulting curve depicts the market’s expectations of future interest rates and provides valuable information about the current and anticipated economic environment.
Treasury Yield Curve Overview: A Treasury Yield Curve Plots Treasury Interest Rates Relative To:
A treasury yield curve is a graphical representation of the interest rates on Treasury securities with different maturities. It plots the yield (interest rate) on the y-axis against the maturity (time to maturity) on the x-axis. The yield curve provides insights into the market’s expectations for future interest rates and economic conditions.
An example of a yield curve is shown below:
- Short-term rates:These are the interest rates on securities with maturities of less than one year.
- Intermediate-term rates:These are the interest rates on securities with maturities of one to ten years.
- Long-term rates:These are the interest rates on securities with maturities of ten years or more.
The shape of the yield curve can vary depending on market conditions and economic expectations. The most common types of yield curves are:
- Normal yield curve:This is a yield curve where short-term rates are lower than long-term rates, indicating that investors expect interest rates to rise in the future.
- Inverted yield curve:This is a yield curve where short-term rates are higher than long-term rates, indicating that investors expect interest rates to fall in the future.
- Flat yield curve:This is a yield curve where short-term and long-term rates are approximately equal, indicating that investors are uncertain about the future direction of interest rates.
- Expectations of future interest rates:Investors’ expectations about the future direction of interest rates play a major role in shaping the yield curve. If investors expect interest rates to rise in the future, they will demand a higher return on long-term securities, resulting in a steeper yield curve.
- Demand for safe assets:In times of economic uncertainty, investors often flock to safe assets such as Treasury securities. This increased demand can drive up the prices of Treasury securities, resulting in lower yields.
- Government borrowing:The government’s borrowing needs can also affect the shape of the yield curve. If the government needs to borrow more money, it will issue more Treasury securities, which can put downward pressure on yields.
- Manage risk:Investors can use yield curves to assess the risk of different investments. For example, an investor who is concerned about rising interest rates may choose to invest in short-term securities with a lower interest rate risk.
- Maximize returns:Investors can use yield curves to identify investment opportunities with the potential for higher returns. For example, an investor who expects interest rates to fall in the future may choose to invest in long-term securities with a higher interest rate.
- Economic conditions:The economic conditions in a country can have a major impact on the shape of its yield curve. For example, a country with a strong economy and low inflation is likely to have a steep yield curve, while a country with a weak economy and high inflation is likely to have a flat or inverted yield curve.
- Government borrowing:The government’s borrowing needs can also affect the shape of the yield curve. A country with a large budget deficit is likely to have a higher demand for Treasury securities, which can drive up yields.
- Monetary policy:The monetary policy of a country’s central bank can also affect the shape of the yield curve. A central bank that is raising interest rates is likely to cause the yield curve to steepen, while a central bank that is cutting interest rates is likely to cause the yield curve to flatten.
Relationship between Treasury Interest Rates and Maturity
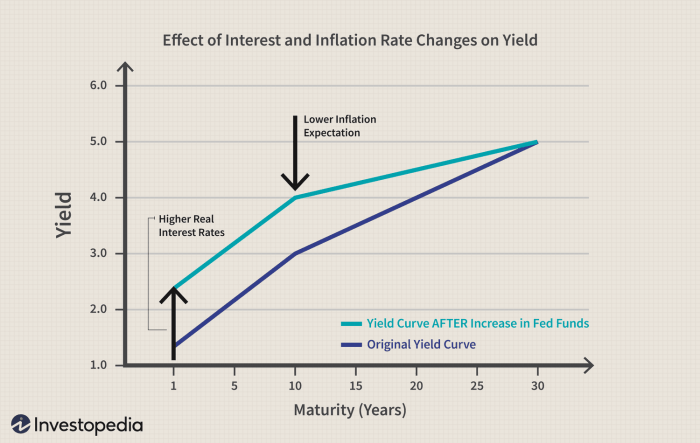
Treasury interest rates are plotted relative to maturity on a yield curve because the maturity of a security is a key factor that determines its interest rate. Longer-term securities generally have higher interest rates than shorter-term securities, as investors require a higher return to compensate them for the risk of holding a security for a longer period.
The shape of the yield curve is influenced by a number of factors, including:
The slope of the yield curve is also an important indicator of economic conditions. A steep yield curve is often associated with economic growth and rising inflation, while an inverted yield curve is often associated with economic recession.
Yield Curve Analysis
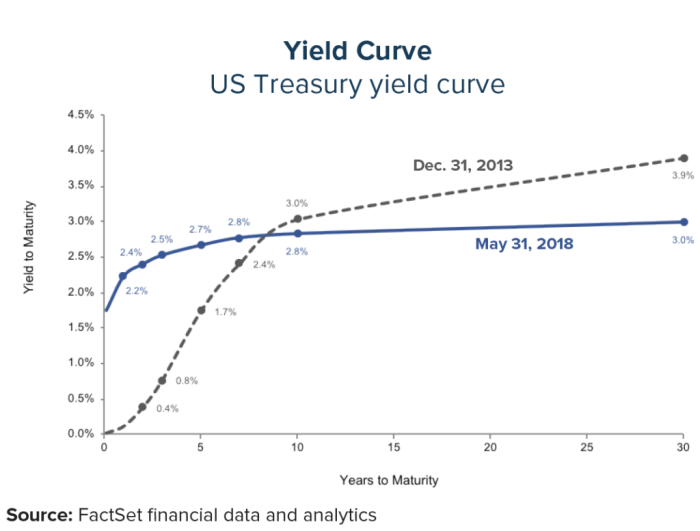
Yield curve analysis is the study of the shape and slope of the yield curve to forecast economic trends. Yield curve inversions, in particular, have historically been a reliable predictor of recessions. For example, the yield curve inverted in 2006 and 2007, which preceded the Great Recession of 2008.
However, it is important to note that yield curve analysis is not a perfect predictor of economic conditions. There have been instances where the yield curve has inverted without a recession following, and there have been instances where a recession has occurred without a yield curve inversion.
Therefore, it is important to consider other economic indicators in conjunction with yield curve analysis when making economic forecasts.
Applications of Treasury Yield Curves
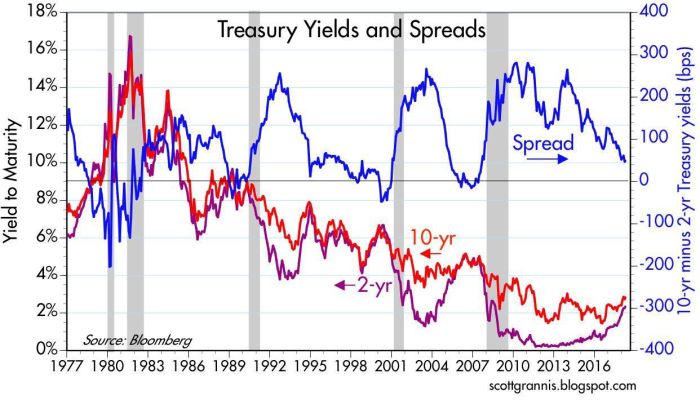
Treasury yield curves have a number of applications in portfolio management and investment decision-making. For example, investors can use yield curves to:
Treasury yield curves also play an important role in setting interest rates and monetary policy. The Federal Reserve uses the yield curve to help determine the target federal funds rate, which is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans.
By adjusting the target federal funds rate, the Fed can influence the overall level of interest rates in the economy.
Global Treasury Yield Curves
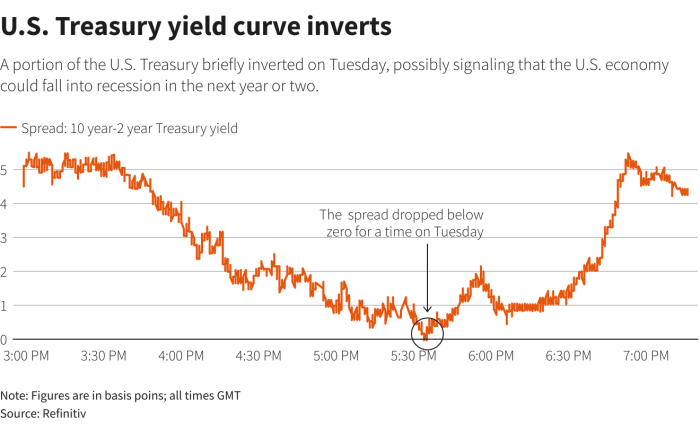
Treasury yield curves from different countries can vary significantly due to a number of factors, including:
Differences in yield curves across countries can have implications for international investors. For example, an investor who expects interest rates to rise in the United States may choose to invest in US Treasury securities, while an investor who expects interest rates to fall in Europe may choose to invest in European Treasury securities.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of the slope of a yield curve?
The slope of a yield curve indicates the market’s expectations for future interest rates. A positive slope suggests that investors anticipate higher interest rates in the future, while a negative slope implies expectations of lower interest rates.
How can yield curve analysis be used to predict economic recessions?
Yield curve inversions, where short-term interest rates exceed long-term interest rates, have historically been associated with increased risk of economic recessions. This is because an inverted yield curve indicates that investors expect lower future economic growth and demand for borrowing.
What are the limitations of using yield curve analysis for economic forecasting?
While yield curve analysis can provide valuable insights, it is important to note that it is not a foolproof method for predicting economic events. Yield curve movements can be influenced by various factors, including market sentiment, geopolitical events, and central bank policies.
