If your hospital laboratory isolates Streptococcus pneumoniae from four patients, it’s a cause for concern. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacterium that can cause a variety of infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. In this article, we will discuss the identification, characteristics, epidemiology, transmission, clinical manifestations, complications, antimicrobial susceptibility, resistance, infection control, and prevention of Streptococcus pneumoniae infections.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive, encapsulated bacterium that is a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. The bacterium is spread through respiratory droplets and can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild respiratory illness to severe, life-threatening infections.
Streptococcus pneumoniae Identification and Characteristics
The isolation of Streptococcus pneumoniaefrom patient samples is significant because it can cause various infections, including pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. It is a Gram-positive, lancet-shaped bacterium that typically appears in pairs or chains under a microscope.
Laboratory Techniques for Identifying Streptococcus pneumoniae
Identification of S. pneumoniaeinvolves several laboratory techniques:
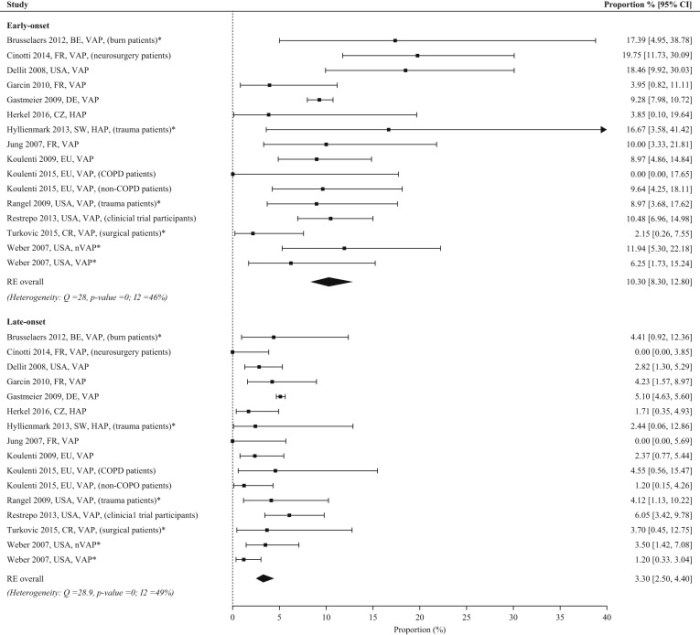
- Gram staining:Differentiates Gram-positive from Gram-negative bacteria.
- Optochin susceptibility:Distinguishes S. pneumoniaefrom other alpha-hemolytic streptococci.
- Bile solubility test:Confirms the presence of choline-containing teichoic acids, a characteristic of S. pneumoniae.
Epidemiology and Transmission
Streptococcus pneumoniaeis a common bacterium found in the respiratory tract of healthy individuals. It is spread through respiratory droplets, such as coughing or sneezing.
Risk Factors and Susceptible Populations, If your hospital laboratory isolates streptococcus pneumoniae from four patients
Risk factors for S. pneumoniaeinfections include:
- Young children and the elderly
- Immunocompromised individuals
- Smokers
- Individuals with chronic respiratory conditions
Clinical Manifestations and Complications: If Your Hospital Laboratory Isolates Streptococcus Pneumoniae From Four Patients
Streptococcus pneumoniaeinfections can manifest as:
- Pneumonia:Inflammation of the lung tissue
- Meningitis:Inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord
- Sepsis:A life-threatening condition caused by the body’s response to infection
Complications and Severity
Complications of S. pneumoniaeinfections can include:
- Pleural effusion (fluid accumulation in the lungs)
- Empyema (pus accumulation in the lungs)
- Brain abscess (pus accumulation in the brain)
- Permanent neurological damage
The severity of S. pneumoniaeinfections varies depending on the patient’s immune status, the site of infection, and the strain of bacteria.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance
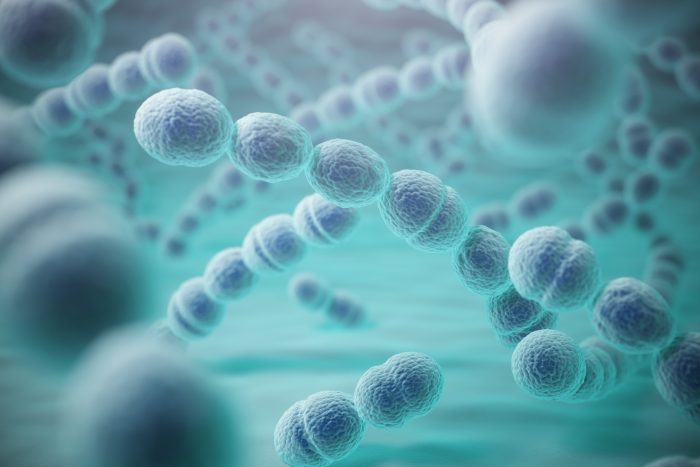
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is crucial for guiding treatment decisions for S. pneumoniaeinfections.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns
S. pneumoniaehas shown increasing resistance to antibiotics, including penicillin and macrolides.
Mechanisms of Resistance
Mechanisms of resistance in S. pneumoniaeinclude:
- Alteration of penicillin-binding proteins
- Efflux pumps
- Mutation of ribosomal RNA
Infection Control and Prevention
Infection control measures are essential to prevent the spread of S. pneumoniae.
Vaccination
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent S. pneumoniaeinfections. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) is recommended for children and adults with certain risk factors.
Antibiotic Stewardship
Antibiotic stewardship is crucial to reduce antimicrobial resistance. Appropriate antibiotic selection and duration of therapy are essential.
Hand Hygiene and Respiratory Etiquette
Proper hand hygiene and respiratory etiquette, such as covering coughs and sneezes, can help prevent the transmission of S. pneumoniae.
Questions Often Asked
What are the symptoms of Streptococcus pneumoniae infections?
The symptoms of Streptococcus pneumoniae infections can vary depending on the type of infection. Common symptoms include fever, chills, cough, shortness of breath, and headache. In severe cases, Streptococcus pneumoniae infections can lead to pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis.
How is Streptococcus pneumoniae spread?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is spread through respiratory droplets. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, they release droplets that can contain the bacteria. These droplets can be inhaled by others, who can then become infected.
How can Streptococcus pneumoniae infections be prevented?
There are a number of things that can be done to prevent the spread of Streptococcus pneumoniae, including:
- Vaccination
- Good hygiene
- Antibiotic stewardship