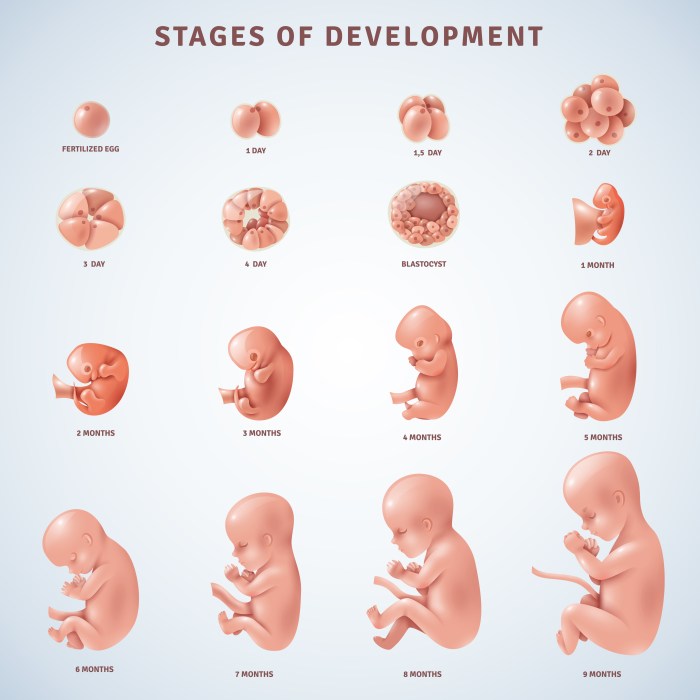
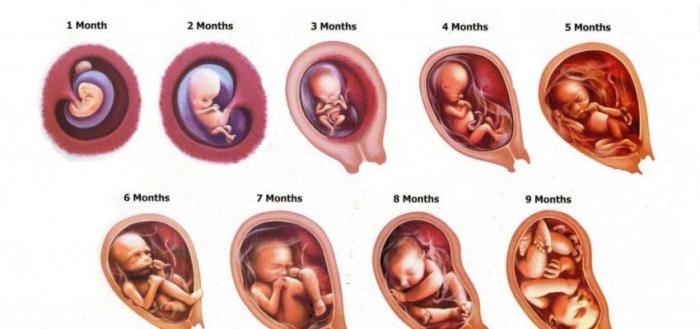
The development of a human fetus lab presents a fascinating and complex subject that has profound implications for our understanding of human biology, reproductive health, and the future of medicine. This guide delves into the intricacies of fetal development, exploring the laboratory techniques employed to study it and the ethical considerations that arise in this field of research.
As we delve into the topic, we will examine the factors influencing fetal development, discuss the applications of fetal development research in prenatal care and beyond, and explore the perspectives of various stakeholders on the ethical issues involved in this groundbreaking field.
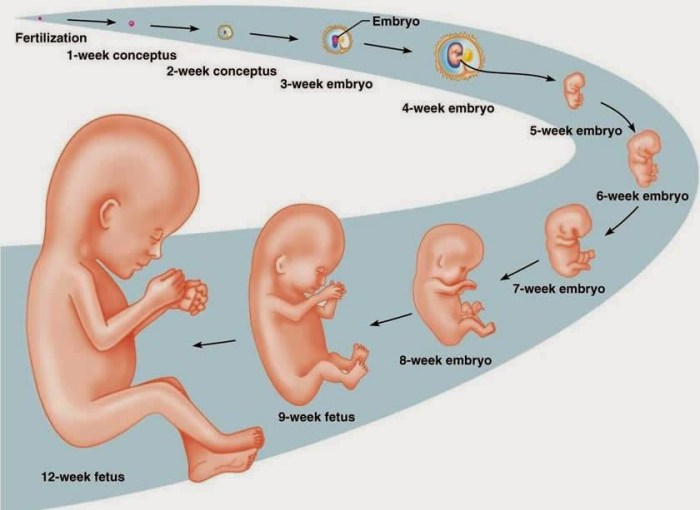
Fetal Development Timeline: Development Of A Human Fetus Lab
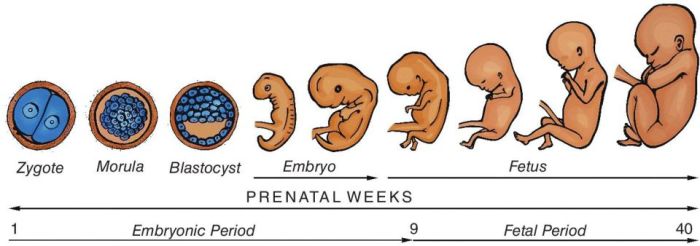
Human fetal development is a complex process that spans from conception to birth. During this period, the fertilized egg undergoes a series of remarkable transformations, developing from a single-celled zygote into a fully formed fetus. The development process is divided into three main stages: the embryonic stage, the fetal stage, and the perinatal stage.
The embryonic stage begins at conception and lasts until the eighth week of pregnancy. During this stage, the fertilized egg implants in the uterine wall and begins to divide rapidly, forming a blastocyst. The blastocyst then differentiates into the inner cell mass, which will develop into the fetus, and the outer trophoblast, which will form the placenta.
The fetal stage begins at the ninth week of pregnancy and lasts until the 37th week. During this stage, the fetus grows rapidly and begins to develop its organs and systems. By the end of the fetal stage, the fetus is fully formed and capable of surviving outside the womb.
The perinatal stage begins at the 37th week of pregnancy and lasts until the first few days after birth. During this stage, the fetus prepares for birth and begins to make the transition to life outside the womb.
Factors Influencing Fetal Development
A number of factors can influence fetal development, including:
- Genetics:The genes inherited from both parents play a major role in determining the fetus’s physical characteristics, as well as its susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Environmental factors:The mother’s environment during pregnancy can also have a significant impact on fetal development. Exposure to certain toxins, such as alcohol, drugs, and tobacco smoke, can increase the risk of birth defects and other health problems.
- Maternal health:The mother’s overall health can also affect fetal development. Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and infections can all increase the risk of complications during pregnancy.
Laboratory Techniques for Studying Fetal Development
Studying fetal development in the laboratory is crucial for understanding the complex processes involved in human reproduction and development. Various techniques are employed to investigate different aspects of fetal development, each with its advantages and limitations.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF involves the fertilization of an egg outside the body in a laboratory setting. This technique allows for the study of early embryonic development, including fertilization, cell division, and blastocyst formation. IVF also enables genetic testing of embryos before implantation, reducing the risk of genetic disorders in offspring.
Advantages:Controlled environment, precise observation, and genetic testing.
Limitations:Artificial environment may not fully replicate in vivo conditions, and ethical concerns regarding the use of human embryos.
Embryo Culture
Embryo culture involves maintaining embryos in a laboratory setting to observe their development over time. This technique allows for the study of cell differentiation, organogenesis, and the effects of environmental factors on embryonic development.
Advantages:Detailed observation of developmental processes, ability to manipulate culture conditions.
Limitations:Limited time frame of observation, difficulty in replicating in utero conditions.
Animal Models
Animal models, particularly mice and non-human primates, are used to study fetal development in a living organism. Animal studies provide insights into developmental processes, genetic influences, and the effects of environmental factors on fetal growth and development.
Advantages:Whole-organism approach, ability to study long-term effects, and genetic manipulation.
Limitations:Species differences may limit the applicability of findings to humans, ethical concerns regarding animal experimentation.
Ethical Considerations
Laboratory studies of fetal development raise ethical concerns regarding the use of human embryos and animal models. Researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines to ensure the responsible and respectful use of research materials. Informed consent, transparency, and the minimization of harm to embryos and animals are essential.
Applications of Fetal Development Research
Research on fetal development has significantly advanced our understanding of human reproduction and provided valuable insights for improving prenatal care and treatment.Advances in prenatal care have been made possible by a deeper understanding of fetal development. This includes the development of prenatal screening tests to detect birth defects and genetic disorders, as well as the development of interventions to prevent or treat these conditions.
Understanding Birth Defects and Developmental Disorders, Development of a human fetus lab
Fetal development research has played a crucial role in identifying the causes and risk factors for birth defects and developmental disorders. By studying the intricate processes of fetal development, researchers have gained insights into the genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that can disrupt normal development.
This knowledge has led to the development of targeted interventions and preventive measures to reduce the incidence of these conditions.
Reproductive Health and Family Planning
Fetal development research has implications for reproductive health and family planning. By understanding the factors that influence fetal growth and development, researchers can develop strategies to optimize reproductive outcomes. This includes developing methods for contraception, assisted reproductive technologies, and prenatal counseling to support informed decision-making by prospective parents.
Ethical Issues in Fetal Development Research
Fetal development research involves the study of the development of a human embryo or fetus. This research has the potential to provide valuable insights into human development and disease, but it also raises a number of ethical issues.One of the most significant ethical issues in fetal development research is the use of human embryos.
Human embryos are considered to be potential human beings, and some people believe that it is wrong to use them for research purposes. Others argue that the potential benefits of fetal development research outweigh the ethical concerns, and that it is important to use human embryos in order to gain a better understanding of human development.Another
ethical issue in fetal development research is the potential for harm to the fetus. Fetal development research often involves invasive procedures, such as amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling. These procedures can pose a risk to the fetus, and it is important to weigh the potential benefits of the research against the risks to the fetus.The
ethical issues in fetal development research are complex and there is no easy answer. It is important to consider all of the ethical issues involved before conducting fetal development research, and to weigh the potential benefits of the research against the potential risks.
Ethical Guidelines and Regulations
There are a number of ethical guidelines and regulations that govern fetal development research. These guidelines and regulations are designed to protect the rights of the fetus and to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and ethical manner.One
of the most important ethical guidelines for fetal development research is the principle of informed consent. Informed consent means that the pregnant woman must be fully informed about the risks and benefits of the research before she agrees to participate.
The pregnant woman must also be given the opportunity to ask questions and to make her own decision about whether or not to participate in the research.Another important ethical guideline for fetal development research is the principle of beneficence. Beneficence means that the research must be designed to benefit the fetus.
The research must not pose any unnecessary risks to the fetus, and it must be conducted in a way that is likely to benefit the fetus.The ethical guidelines and regulations for fetal development research are constantly being updated as new research is conducted.
It is important to stay up-to-date on the latest ethical guidelines and regulations in order to ensure that your research is conducted in a responsible and ethical manner.
Perspectives of Different Stakeholders
There are a variety of different stakeholders who have an interest in fetal development research. These stakeholders include scientists, ethicists, patient advocates, and the general public.Scientists are interested in fetal development research because it can provide valuable insights into human development and disease.
Scientists believe that fetal development research has the potential to lead to new treatments for a variety of diseases, including birth defects, genetic disorders, and cancer.Ethicists are interested in fetal development research because it raises a number of ethical issues.
Ethicists believe that it is important to consider the ethical implications of fetal development research before it is conducted. Ethicists work to develop ethical guidelines and regulations for fetal development research.Patient advocates are interested in fetal development research because it has the potential to lead to new treatments for diseases that affect pregnant women and their babies.
Patient advocates work to ensure that the voices of pregnant women and their babies are heard in the debate over fetal development research.The general public is interested in fetal development research because it has the potential to impact the lives of everyone.
The general public has a right to know about the ethical issues involved in fetal development research and to make their voices heard in the debate over this research.
FAQ Section
What are the key stages of human fetal development?
Human fetal development can be divided into three main stages: the embryonic stage (weeks 1-8), the fetal stage (weeks 9-28), and the late fetal stage (weeks 29-40).
How are laboratory techniques used to study fetal development?
Laboratory techniques such as in vitro fertilization, embryo culture, and animal models allow researchers to study fetal development outside the womb, enabling detailed observations and experimentation.
What are the ethical considerations in fetal development research?
Ethical considerations include the use of human embryos, the potential for harm to the fetus, and the need for informed consent from parents.